Sanitary fittings are used in piping systems to connect straight pipes or pipe sections, adapt to different sizes or shapes and for other purposes, such as regulating or measuring fluid flow. “Plumbing” is generally used to describe the transport of water, gas or liquid waste in domestic or commercial environments; “Piping” is often used to describe the transport of high performance fluids (high pressure, high flow, high temperature or hazardous materials) in specialized applications. “Tubing” is sometimes used for lighter pipes, especially those flexible enough to be supplied in rolled form.
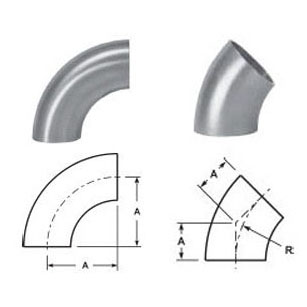
Sanitary fittings (especially unusual types) require money, time, materials and tools to install. They are an important part of piping and plumbing systems. Faucets are technically fittings, but are usually discussed separately. Codes B31.3 and B31.4 have requirements for piping in petroleum refineries; chemical, pharmaceutical, textile, paper, semiconductor and cryogenics plants, as well as processing plants and related terminals. These codes specify requirements for materials and components, design, fabrication, assembly, assembly, inspection, inspection and testing of piping. The codes are applicable to piping for all fluids, including raw, intermediate and finished chemicals; oil products; gas, steam, air and water; fluidized solids; refrigerants and cryogenic fluids.



